43 adipose tissue with labels
Adipocyte Membrane - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Max Lafontan, Michel Berlan, in New Perspectives in Adipose Tissue, 1985. 7.2.3.1 General considerations of the fat cell plasma membrane composition. The protein and glycoprotein components of the fat cell membranes from rat, rabbit and calf were analysed by Kawai and Spiro (1977a).The amino acid composition of the plasma membranes and a major glycoprotein component (apparent relative ... Effect of tirzepatide versus insulin degludec on liver fat content and ... Background: Tirzepatide is a novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist under development for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The aim of this substudy was to characterise the changes in liver fat content (LFC), volume of visceral adipose tissue (VAT), and abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue (ASAT) in response to tirzepatide or ...
Adipose Tissue - The Definitive Guide| Biology Dictionary Adipose tissue is split into two main types of connective tissue - white and brown - that store and burn energy respectively. White adipose tissue also provide a layer of insulation, while brown adipose is found in too small quantities (in children and adults) to do this. Brown fat does, however, release energy in the form of heat.

Adipose tissue with labels
Identification and characterization of adipose surface epitopes Adipose tissue plays a central role in maintaining whole-body glucose and lipid homeostasis and the adipocyte cell surface is the central hub integrating various environmental and endocrine inputs to orchestrate its function. Moreover, the cell surface of adipocytes is the key target for future therapeutic attempts aiming to selectively deliver ... Solved II. Connective Tissues A. Draw and label one loose | Chegg.com Connective Tissues A. Draw and label one loose connective tissue (areolar or adipose) and one cartilage connective tissue (hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, or fibrocartilage). Use the Anatomy and Physiology Revealed program to assist in your drawings. *Each tissue should contain labels of the structures identified on page 5 of the lab manual. Adipose Tissue: Function, Location & Definition - Study.com Adipose is a loose connective tissue that fills up space between organs and tissues and provides structural and metabolic support. It is part of the nutrient glue that holds us all together....
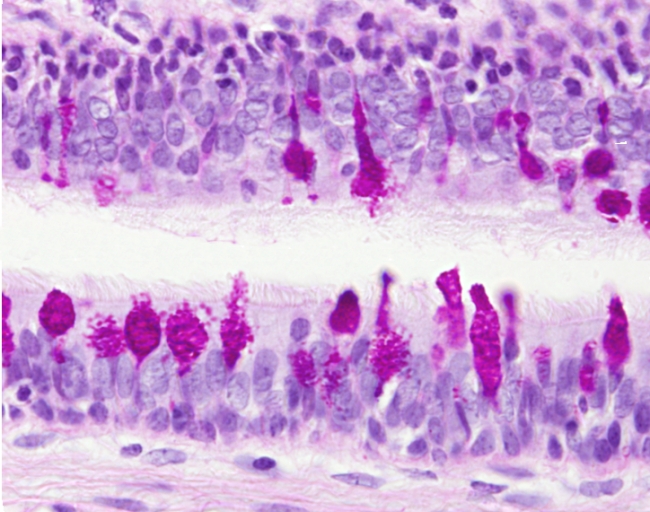
Adipose tissue with labels. Adipose Tissue - Meaning, Types, Functions, and FAQs Adipose tissue is a special and different type of connective tissue, mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes are classified into three types: white adipocytes, brown adipocytes, and beige adipocytes. Their structure, location, and function are different. Brown Adipocytes - Yale University Brown adipose tissue is typically found in large amounts in newborns and some hibernating animals and is important as a source of energy. The cells in brown fat contain numerous and very distinct lipid droplets. The presence of an uncoupling protein in these cells causes the generation of heat that allows for non-shivering thermogenesis. meat processing | Definition, Equipment, Techniques, Products, Mar 30, 2022 · meat processing, preparation of meat for human consumption. Meat is the common term used to describe the edible portion of animal tissues and any processed or manufactured products prepared from these tissues. Meats are often classified by the type of animal from which they are taken. Red meat refers to the meat taken from mammals, white … Skin and hypodermis - Eugraph The skin consists of two layers, the epidermis and the dermis. Below the skin is a layer of areolar/adipose tissue called the hypodermis (or subcutaneous layer). The 40X image shows: e = epidermis. d = dermis. h = hypodermis. sw = sweat gland. seb = sebaceous gland. hf = hair follicle. p = papillary layer of dermis. r = reticular layer of dermis
Fat Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com Fat definition, having too much flabby tissue; corpulent; obese: a fat person. See more. How Adipose Tissue Works - Terumo BCT Process Adipose Tissue Into a Purified MSC-Rich Graft in Just 4 Minutes 1. The AdiPrep ® Adipose Concentration System concentrates tissue samples to deliver a graft with high stem cell and nucleated cell counts while significantly reducing excess fluid that contribute to graft volume loss. The resulting purified adipose concentrate can then be ... Lab Notes Home Page - Kentucky Community and Technical College System Adipose Tissue (fat) Tightly packed & highly vascularized An oil droplet pushes the nucleus to one side. iii). ... that form a 3-dimensional network . Areolar Connective Tissue: Adipose Tissue: Reticular Connective Tissue: LABEL: fibroblast cell. elastic fibers. collagen fibers. LABEL: fat storage area. nucleus. LABEL. white blood cells Origin and Functions of Tissue Macrophages - PMC Jul 17, 2014 · Recruitment and proliferation appear to be intertwined. Macrophage proliferation in adipose tissue has been reported to be dependent on MCP-1, as is monocyte emigration from bone marrow and entry into circulation and peripheral tissue (Serbina and Pamer, 2006; Amano et al., 2014). As opposed to the idea that MCP-1-CCR2 signaling in adipose ...
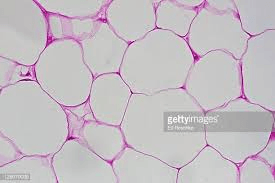
Noninvasive Detection of Inflammatory Changes in White Adipose Tissue ... White adipose tissue inflammation (WATi) has been linked to the pathogenesis of obesity-related diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. ... Noninvasive Detection of Inflammatory Changes in White Adipose Tissue by Label-Free Raman Spectroscopy Anal Chem. 2016 Feb 16;88(4):2140-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03696. Adipose connective tissue - Austin Community College District Adipose connective tissue 400X The bar labeled "a" indicates the width of one adipose cell (adipocyte). The light purple dots you see inside the cells are an artifact of process used to make the images, and do not represent real structures. The arrow points to the nucleus of one adipocyte. Scar - Wikipedia Scar; Scar tissue on an arm: Specialty: Dermatology, plastic surgery: A scar is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after ... quizlet.com › 529392371 › ap-flash-cardsAP Flashcards | Quizlet Classify the body location/structure with the correct type of connective tissue by clicking and dragging the labels from column A to the appropriate location in column B. adipose -subcutaneous layer
Adipose Tissue - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Abstract. Adipose tissue (AT) is a very active organ, both metabolically and hormonally. These important functions depend on adequate blood flow (BF). Metabolic, hormonal, and vascular processes within AT are highly interconnected and any disruption will invariably impact the others.
Label-free profiling of white adipose tissue of rats exhibiting high or ... We analysed visceral adipose tissue of HCR and LCR using label-free HDMS E profiling. The running capacity of HCR was 9-fold greater than LCR. Proteome profiling encompassed 448 proteins and detected 30 significant (p <0.05; false discovery rate <10%, calculated using q-values) differences. Approximately half of the proteins analysed were of ...
Adipose tissue: a fat lot of good? | Society for Endocrinology 3D rendering of a 100-µm thick section of murine adipose tissue in the kidney. Immunofluorescent staining for the lipid droplet protein perilipin is in cyan. A lineage tracing Cre-induced tdTomato fluorescent protein labels a subset of adipocytes red. In the centre, the nucleus of a resident adipose stem cell is labelled green. ©J. Rochford
Chapter 25 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the major renal processes and associated nephron structures. ... The fibrous capsule is a layer of adipose tissue that surrounds the kidney. Renal cortex. Which region of the kidney is the most superficial? Renal cortex.
Labeled Tissues Flashcards | Quizlet Adipose Tissue Label ground substance, elastic fibers, collagen fibers, fat droplet, specific cells of each tissue Dense ( White) Regular Tissue Label ground substance, elastic fibers, collagen fibers, fat droplet, specific cells of each tissue Hyaline Cartilage
The developmental origins of adipose tissue Adipose tissue is formed at stereotypic times and locations in a diverse array of organisms. Once formed, the tissue is dynamic, responding to homeostatic and external cues and capable of a 15-fold expansion. The formation and maintenance of adipose tissue is essential to many biological processes and when perturbed leads to significant diseases.
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1): a growth hormone - PMC IGF-1. IGF-1 and IGF-2 were identified in 1957 by Salmon and Daughaday 8 and designated “sulphation factor” by their ability to stimulate 35-sulphate incorporation into rat cartilage.Froesch et al described the non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) of two soluble serum components (NSILA I and II). 9 In 1972, the labels sulphation factor and NSILA were replaced by the term ...
Adipose Tissue Histology Brown adipose tissue (labels) - histology slide: Adipose tissue, mouse - histology slide: Adipose tissue - histology slide: Adipose tissue - histology slide: ... Adipose tissue - histology slide: Adipose tissue - histology slide: Adipose tissue - histology slide: Adipose tissue - histology slide: 27 files on 3 page(s) 1: 2: 3: Powered by ...
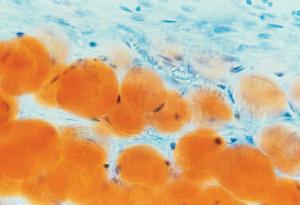
Adipose connective tissue - University of Wisconsin-La Crosse Adipose connective tissue 1. Cell membrane 2. Cell nucleus 3. Fat vacuoles Adipose connective tissue cells are specialized for fat storage and do not form ground substance or fibers. On prepared slides, adipose tissue appears somewhat like a fish net with white spaces connected together in a network.
Adipose Tissue - Physiopedia Adipose tissue acts as an endocrine system organ by generating hormones that influence metabolic activity in other organ systems. Some of the hormones produced by adipose cells influence sex hormone metabolism, blood pressure regulation, insulin sensitivity, fat storage and use, blood clotting, and cell signaling.Adipose tissue performs these vital roles by secreting several biologically ...
Adipose tissue - Vida Private Label Our formulations, which are designed to work on adipocytes, are based on active ingredients containing xanthines, such as caffeine and theophylline, known for their beneficial remodelling action on fat cells, and sodium deoxycholate.
Solved Label the components of adipose tissue. Fibroblast | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Label the components of adipose tissue. Fibroblast Cell membrane Elastic fiber Nucleus Adipocyte Fibroblast Cell membrane Elastic fiber Nucleus Adipocyte Previous question Next question
Lipids – Nutrition Essentials - Maricopa Understanding Food Labels and Health Claims. 6. Essential Nutrients. 7. The Process of Digestion and Absorption. 8. Carbohdyrates. 9. Lipids. 10. Protein. 11. Food Allergies. 12. Vitamins. ... Still, adipose tissue can comprise a much larger percentage of bodyweight depending on the degree of obesity of the individual.
Adipose Tissue: What Is It, Location, Function, and More - Osmosis Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that arises from the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes during fetal development. Mesenchymal stem cells are pluripotent cells that can transform into various cell types, including fat cells, bone cells, cartilage cells, and muscle cells, among others.
Adipose tissue - Wikipedia Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages.
Adipose Tissue - Composition, Location and Function Adipose, or fat, tissue is loose connective tissue composed of fat cells known as adipocytes. Adipocytes contain lipid droplets of stored triglycerides. These cells swell as they store fat and shrink when the fat is used for energy. Adipose tissue helps to store energy in the form of fat, cushion internal organs, and insulate the body.






Post a Comment for "43 adipose tissue with labels"